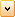
The audit trail is designed to track changes applied to a data. Audit trail is a must be feature in modern software and is also included in many official regulations.
Audit trail can be implemented on individual writable statement. This provides the developer with option to control the data and its changes. The configuration of audit trail takes place in design time and in runtime. In design time developer defines entity, primary key and data to be displayed in audit trail viewer. In contradiction to Electronic Signature no security policy needs to be defined. This means that with a few simple clicks advanced and complex feature such as audit trail is implemented.
The result of audit trail implementation can be viewed in Audit Trail viewer. User, with appropriate credentials, can access the viewer by right clicking on the grid in the desired row and selecting Audit Trail... option. The grid must contain data from the data source where audit trail is implemented. A window appears containing all entities for the data source. In the list Supported Entities check the entity for which you wish to view data. The viewer provides following data
| Column | Description |
|---|---|
| Entity | A short description of the entity |
| Timestamp | Date and time when the change occurred. |
| User | First and last name of the user that changed the value. |
| Field | String defined in design time with property Caption. Column should contain information about the parameter or the field that is tracked. |
| Value | The new value for the field in the selected record in a grid. |
| Workstation | Workstation name or the name of the computer where the change was made. |
| Client | The application in which the change was made. |
Trailing can be defined for a field or for a parameter. To create trail items several commands are available
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
| Add | Adds the desired type of trail item for the selected statement. Created item is added to the list in section Existing Items. |
| Remove | Removes trail item selected in Existing Items list. |
| Clear | Removes all trail items in Existing Items list. |
Two types of trail items are available, field and parameter trail. Field trail protects a field in the schema from being modified. Parameter trail protects a parameter for the statement. The main difference between these two trail items is that parameter trail item is protected directly. This is useful in cases when it is not necessary that a field will change the value of a parameter. The value of a parameter can also be changed by other means such as workflow. For this case parameter trail item was introduced.
The appearance, bindings and data is defined with properties.
Parameter Trail Item
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Caption | Defines the value of the column Field in Audit Trail viewer. Value of this property should provide information about the parameter. |
| EntityCode | Defines a unique value by which it is possible to define security policy. |
| KeyParameter | Defines the parameter that serves as a primary key for a data source. |
| ParameterName | Defines the parameter whose value will be displayed in Audit Trail viewer in order to see the new value. |
Field Trail Item
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Caption | Defines the value of the column Field in Audit Trail viewer. Value of this property should provide information about the field. |
| EntityCode | Defines a unique value by which it is possible to define security policy. |
| DisplayMember | Defines the field whose value will be displayed in the Audit Trail viewer. |
| KeyMember | Defines the field which represents primary key in a schema of a data source. |
| ValueMember | Defines the field whose value will be used to create the change. |